WheatGOAT: Measurement System
Introduction
WheatGOAT has five main parts: a backbone to extract features, an Object-Background Selector (OBS) to separate wheat ears from the background, an Object Perception Learner (OPL) that uses vision-language models to better identify small or overlapping ears, a Hierarchical Refiner (HR) to improve detail using multi-scale context, and a Prediction Module (PM) that creates a precise density map for counting. This design boosts accuracy and works well in varied field conditions and crop types.
Dependencies
- CUDA 11.8
- Python 3.8 (or later)
- torch==1.13.1
- torchaudio==0.13.1
- torchcam==0.3.2
- torchgeo==0.4.1
- torchmetrics==0.11.4
- torchvision==0.14.1
- numpy==1.21.6
- Pillow==9.2.0
- einops==0.6.0
- opencv-python==4.6.0.66
GitHub: https://github.com/GZU-SAMLab/WheatGOAT
Code and Data
The code can be downloaded from there. We use the global wheat Head Detection 2021 (dataset) for training. The density map is marked in the annotation.zip compressed package.
Pre-trained models
Here are the trained WheatGOAT weights, the first ten layers of VGG16 weights, and the fine-tuned YOLOv8 weights.
Get Started
Training
Step1:Please divide the data set according to the csv file.
Step2:Change the dataset path in the train.py file to the location of the dataset.
Step3:
python train.py
Testing
Step1:Please download the weights in the current directory.
Step2:Please change the relevant path in the test.py file
Step3:
python test.py
Results
Quantitative Analysis
These results demonstrate WheatGOAT’s superior accuracy, robustness, and generalization in complex field conditions, attributed to its object-aware perception and hierarchical refinement strategy.
Figure 1:Quantitative comparison of wheat ear counting performance across different models on the GWHD_2021 dataset.
Visualization of Model Decision-Making
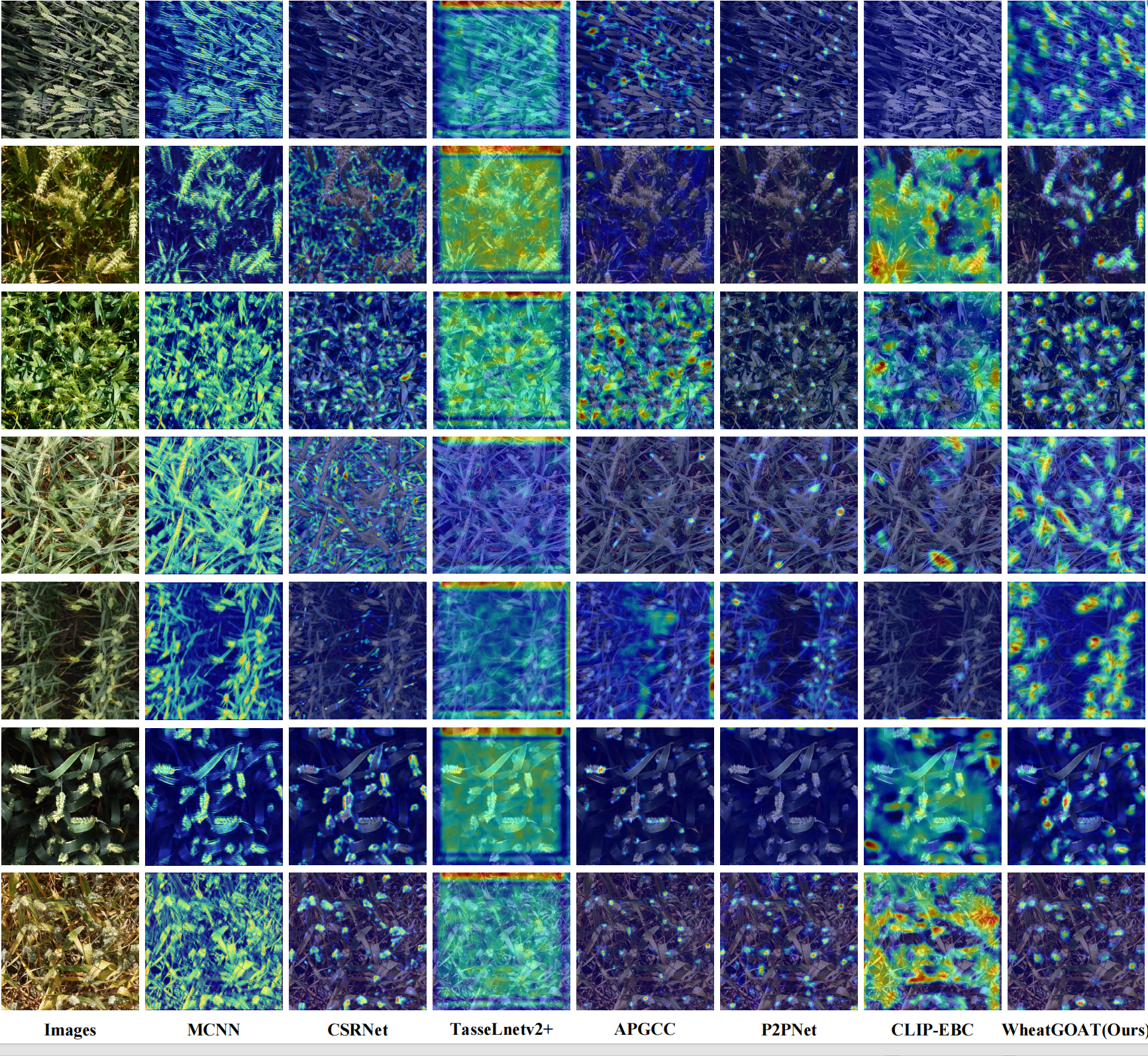
Figure 2: Visualization of model attention using Grad-CAM across various wheat ear counting methods.
